注释
成员
|
你可能有一个错误。Grbl 应该几乎立即执行它收到的任何命令。如果 Grbl 必须快速执行大量非常短的行,它会变慢。这是因为规划器没有足够的距离来加速。查看存储库中的 stream.py 脚本,了解如何编写简单的流媒体。此外,针对 UGS 或 bCNC 等其他 GUI 进行测试以测试性能。 |
作者
|
在 $C 检查模式下一切正常。在那种模式下,我每秒可以处理 400 多行,没有错误或延迟。 |
成员
|
@CliveMcCarthy:是的,因为检查模式不计划任何事情。只是解析。 |
作者
|
似乎,我最多可以每秒将大约 35 行 26 字节的代码从我的代码泵送到 Grbl 中,计划程序(大概)偶尔会在继续之前将事情暂停十分之几秒。事情应该是这样吗?我已经运行了 50,000 行 G 代码,运行中最初的不稳定行为似乎已经稳定下来。规划器是否从给定的代码“风格”中“学习”?在 2017 年 9 月 8 日下午 04:09,Sonny Jeon 写道: @CliveMcCarthy:是的,因为检查模式不计划任何事情。只是解析。— 你收到这个是因为你被提到了。直接回复此电子邮件,在 GitHub 上查看它,或将线程静音。{“api_version”:”1.0″,”publisher”:{“api_key”:”05dde50f1d1a384dd78767c55493e4bb”,”name”:”GitHub”},”entity”:{“external_key”:”github/grbl/grbl”,”title “:”grbl/grbl”,”subtitle”:”GitHub 存储库”,”main_image_url”:” https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/17495839/a5054eac-5d88-11e6-95fc-7290892c7bb5.png” ,”avatar_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/15842166/7c72db34-2c0b-11e6-9aed-b52498112777.png”,#1284:@CliveMcCarthy:是的,因为检查模式不计划任何事情。只需解析。”}],”action”:{“name”:”View Issue”,”url”:” #1284 (comment) “}}}
|
作者
|
经过更多测试后,我似乎可以平均每秒发送 40 行 G 代码,每行 1 毫米,速度为 2,400 毫米/分钟。有最多 12 秒的重复周期性延迟。 |
作者
作者
|
看来我必须等待 ARM 版本:Grbl 没有多少“团队”,因为很长一段时间以来它一直是我自己。v1.0 发布后不久将取消对 8 位的支持。我将继续投入所有时间来继续开发 ARM 版本,这是对 Grbl 基本代码的完全重写。Grbl 本身是专门为 8 位 AVR 设计的,并且有很多“讨厌的”代码是为了最大化性能和减少编译闪存大小而编写的。主要是后者。ARM 版本没有这样的限制,并且有许多算法改进可以使它在基础层面上变得更好。我不会透露它们是什么,但它们会很棒。2017 年 9 月 8 日 04 日: @CliveMcCarthy:是的,因为检查模式不计划任何事情。只是解析。— 你收到这个是因为你被提到了。直接回复此电子邮件,在 GitHub 上查看它,或将线程静音。{“api_version”:”1.0″,”publisher”:{“api_key”:”05dde50f1d1a384dd78767c55493e4bb”,”name”:”GitHub”},”entity”:{“external_key”:”github/grbl/grbl”,”title “:”grbl/grbl”,”subtitle”:”GitHub 存储库”,”main_image_url”:” https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/17495839/a5054eac-5d88-11e6-95fc-7290892c7bb5.png” ,”avatar_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent。https://github.com/grbl/grbl”}},”updates”:{“snippets”:[{“icon”:”PERSON”,”message”:”@chamnit in #1284:@CliveMcCarthy:是的,因为检查模式不计划任何事情。只需解析。”}],”action”:{“name”:”View Issue”,”url”:” #1284 (comment) “}}}
|
成员
|
您是否按我的要求做了并针对信誉良好的 GUI 进行了测试?Grbl 每秒最多可以执行 250 行。就像 wiki 页面状态一样,发送和响应协议并不是最快的。如果您需要更快,请使用字符计数协议。 |
作者
|
我用 UGS 做了一个快速测试,发现它可以在大约一个小时内运行我的测试 G 代码,它有大约 140,000 行。相当满意。我的典型 G 代码行(30 字节)的典型写入用时不到 10 微秒。如果我运行我的测试 G 代码,使用我的程序并打开检查模式,Grbl 的响应通常不到 10 微秒,但通常也需要 4,000 微秒。真的很奇怪,因为这些行非常相似,并且人们会期望解析的时间接近恒定。写入和确认周期时间足够快,这让我确信我的计算机和 Arduino 之间的硬件/软件协议运行正常。如果我在操作模式下运行它,事情就会严重减慢。3 字节读取响应(Grbl 的“确定”确认)的时间变化很大,从最快 5 毫秒返回,通常为 20 毫秒,但通常为 100 毫秒,周期性许多秒。我尝试在读取发生之前的写入之后添加延迟,但它不会改善缓慢的响应。如果写入和确认周期时间始终为 25 毫秒,它将大约等于 UGS 的周期时间。这很奇怪。在 2017 年 9 月 9 日下午 09:52,Sonny Jeon 写道:您是否按我的要求做了并针对信誉良好的 GUI 进行了测试?— 你收到这个是因为你被提到了。直接回复此电子邮件,在 GitHub 上查看它,或将线程静音。{“api_version”:”1.0″,”publisher”:{“api_key”:”05dde50f1d1a384dd78767c55493e4bb”,”name”:”GitHub”},”entity”:{“external_key”:”github/grbl/grbl”,”title “:”grbl/grbl”,”副标题”:”GitHub 存储库”,”main_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/17495839/a5054eac-5d88-11e6-95fc-7290892c7bb5.png”,”avatar_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/15842166/ 7c72db34-2c0b-11e6-9aed-b52498112777.png”,”action”:{“name”:”Open in GitHub”,”url”:” https://github.com/grbl/grbl”}},”updates “:{“snippets”:[{“icon”:”PERSON”,”message”:”@chamnit在#1284中:你是否按照我的要求做了并针对信誉良好的 GUI 进行了测试?”}],”action”:{ “name”:”View Issue”,”url”:” #1284(评论) “}}}
|
作者
作者
|
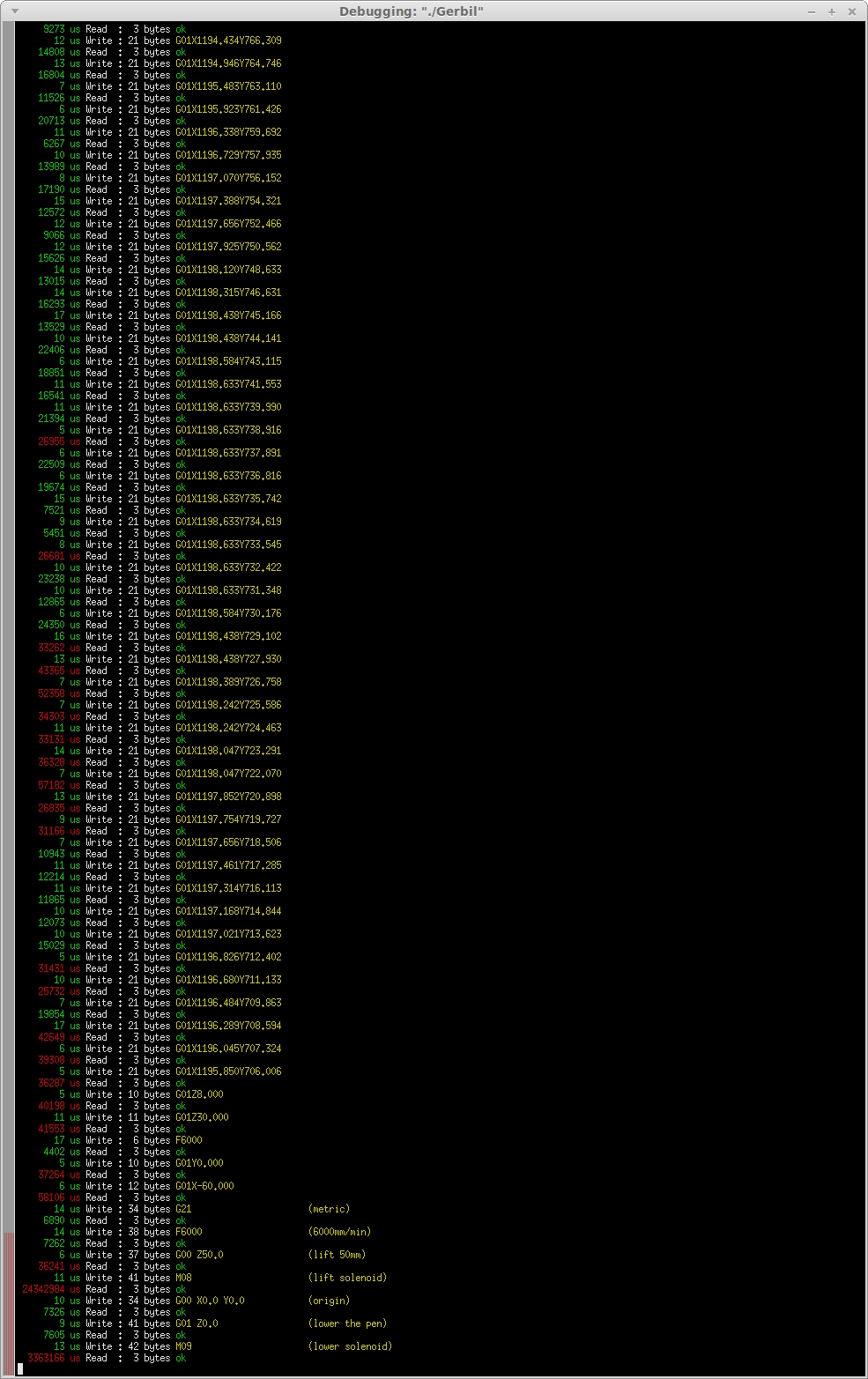
此屏幕截图很好地说明了这些问题。在序列的末尾有一个 M08 指令,Grbl 需要 24 秒来响应。在 2017 年 9 月 9 日下午 09:52,Sonny Jeon 写道: 你是否按照我的要求做了并针对信誉良好的 GUI 进行了测试?— 你收到这个是因为你被提到了。直接回复此电子邮件,在 GitHub 上查看它,或将线程静音。{“api_version”:”1.0″,”publisher”:{“api_key”:”05dde50f1d1a384dd78767c55493e4bb”,”name”:”GitHub”},”entity”:{“external_key”:”github/grbl/grbl”,”title “:”grbl/grbl”,”副标题”:”GitHub 存储库”,”main_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/17495839/a5054eac-5d88-11e6-95fc-7290892c7bb5.png”,”avatar_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/15842166/ 7c72db34-2c0b-11e6-9aed-b52498112777.png”,”action”:{“name”:”Open in GitHub”,”url”:” https://github.com/grbl/grbl”}},”updates “:{“snippets”:[{“icon”:”PERSON”,”message”:”@chamnit在#1284中:你是否按照我的要求做了并针对信誉良好的 GUI 进行了测试?”}],”action”:{ “name”:”View Issue”,”url”:” #1284(评论) “}}}
|
作者
成员
|
将您的 $1 设置设置为 $1=255。Grbl 每秒最多可以处理 400 行。那是每行 2.5 毫秒。不是 25。机器可能会停止,执行步骤延迟,然后恢复。默认值约为 25 毫秒,这可以解释您的问题 |
成员
|
您看到的较长延迟来自您的 g 代码。Grbl 必须在执行需要与运动同步的行之前执行所有缓冲的运动。M8 M9 M30 等都可以作为同步命令。延迟来自等待完成排队的动作。 |
作者
|
这似乎很有帮助。进给率变化是否也算作“与运动同步”,因为每次进给率变化似乎也会导致“失速”?还有其他似乎与任何事情都无关的“摊位”……顺便说一句,感谢您对此的帮助。在 2017/09/11 08:52,Sonny Jeon 写道:将你的 $1 设置设置为 $1=255。Grbl 每秒最多可以处理 400 行。那是每行 2.5 毫秒。不是 25。机器可能会停止,执行步骤延迟,然后恢复。默认值约为 25 毫秒,这可以解释您的问题——您收到此消息是因为有人提到了您。直接回复此电子邮件,在 GitHub 上查看它,或将线程静音。{“api_version”:“1.0”,“发布者”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/17495839/a5054eac-5d88-11e6-95fc-7290892c7bb5.png”,”avatar_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/15842166/ 7c72db34-2c0b-11e6-9aed-b52498112777.png”,”action”:{“name”:”Open in GitHub”,”url”:” https://github.com/grbl/grbl”}},”updates “:{“snippets”:[{“icon”:”PERSON”,”message”:”@chamnit在#1284中:将您的 $1 设置设置为 $1=255。Grbl 每秒最多可以处理 400 行。那是每行 2.5 毫秒。不是 25。机器可能会停止,执行步骤延迟,然后恢复。默认值约为 25 毫秒,这可以解释您的问题\r\n”}],”action”:{“name”:”
|
作者
|
您还有其他 Grbl 建议吗?我每行仍然只有不到 20 毫秒。在 2017/09/11 08:52,Sonny Jeon 写道:将你的 $1 设置设置为 $1=255。Grbl 每秒最多可以处理 400 行。那是每行 2.5 毫秒。不是 25。机器可能会停止,执行步骤延迟,然后恢复。默认值约为 25 毫秒,这可以解释您的问题——您收到此消息是因为有人提到了您。直接回复此电子邮件,在 GitHub 上查看它,或将线程静音。{“api_version”:”1.0″,”publisher”:{“api_key”:”05dde50f1d1a384dd78767c55493e4bb”,”name”:”GitHub”},”entity”:{“external_key”:”github/grbl/grbl”,”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/17495839/a5054eac-5d88-11e6-95fc-7290892c7bb5.png”,”avatar_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/15842166/ 7c72db34-2c0b-11e6-9aed-b52498112777.png”,”action”:{“name”:”Open in GitHub”,”url”:” https://github.com/grbl/grbl”}},”updates “:{“snippets”:[{“icon”:”PERSON”,”message”:”@chamnit在#1284中:将您的 $1 设置设置为 $1=255。Grbl 每秒最多可以处理 400 行。那是每行 2.5 毫秒。不是 25。机器可能会停止,执行步骤延迟,然后恢复。默认值约为 25 毫秒,这可以解释您的问题\r\n”}],”action”:{“name”:”
|
作者
|
我让我的代码计算响应时间的运行平均值。在 60,000 行之后,平均值为 10.8 毫秒。在 2017 年 9 月 11 日上午 09:00,Sonny Jeon 写道: 你看到的更长的延迟来自你的 g 代码。Grbl 必须在执行需要与运动同步的行之前执行所有缓冲的运动。M8 M9 M30 等都可以作为同步命令。— 你收到这个是因为你被提到了。直接回复此电子邮件,在 GitHub 上查看它,或将线程静音。{“api_version”:”1.0″,”publisher”:{“api_key”:”05dde50f1d1a384dd78767c55493e4bb”,”name”:”GitHub”},”entity”:{“external_key”:”github/grbl/grbl”,”title “:”grbl/grbl”,”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/17495839/a5054eac-5d88-11e6-95fc-7290892c7bb5.png”,”avatar_image_url”:”https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/143418/15842166/ 7c72db34-2c0b-11e6-9aed-b52498112777.png”,”action”:{“name”:”Open in GitHub”,”url”:” https://github.com/grbl/grbl”}},”updates “:{“snippets”:[{“icon”:”PERSON”,”message”:”@chamnit在#1284中:您看到的较长延迟来自您的 g 代码。Grbl 必须在执行需要与运动同步的行之前执行所有缓冲的运动。M8 M9 M30 等都符合同步命令的条件。”}],”action”:{“name”:”View Issue”,”url”:”
|
成员
|
您还在使用发送响应协议吗?如果是这样,请使用 UGS 或 GRBL stream.py 脚本再次测试。他们使用字符计数协议。 |
作者
作者
|
I took my 140,000 line test and ran it on UGS with $1=255. The run time was 50 minutes. The run time on my code was 49.8 minutes. I conclude that the character counting helps the Java sender, however, my dumb send-and-acknowledge is probably compensated for by the faster feed from the C program which keeps the pipeline full. UGS also experiences some stalling but, of course, I don’t have numbers, just a visual impression. In another week I shall be able to run this 140,000 line test on our CNC machine with its current driver and software. Then I will know if I can cut over the hardware to the Arduino and Grbl. I hope I can, because I dislike using XP and with a legacy parallel port interface. On 09/11/2017 11:21 AM, Sonny Jeon wrote: Are you still using the send response protocol? If so, test again with UGS or the GRBL stream.py script. They use the character counting protocol. — You are receiving this because you were mentioned. Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub, or mute the thread.
|


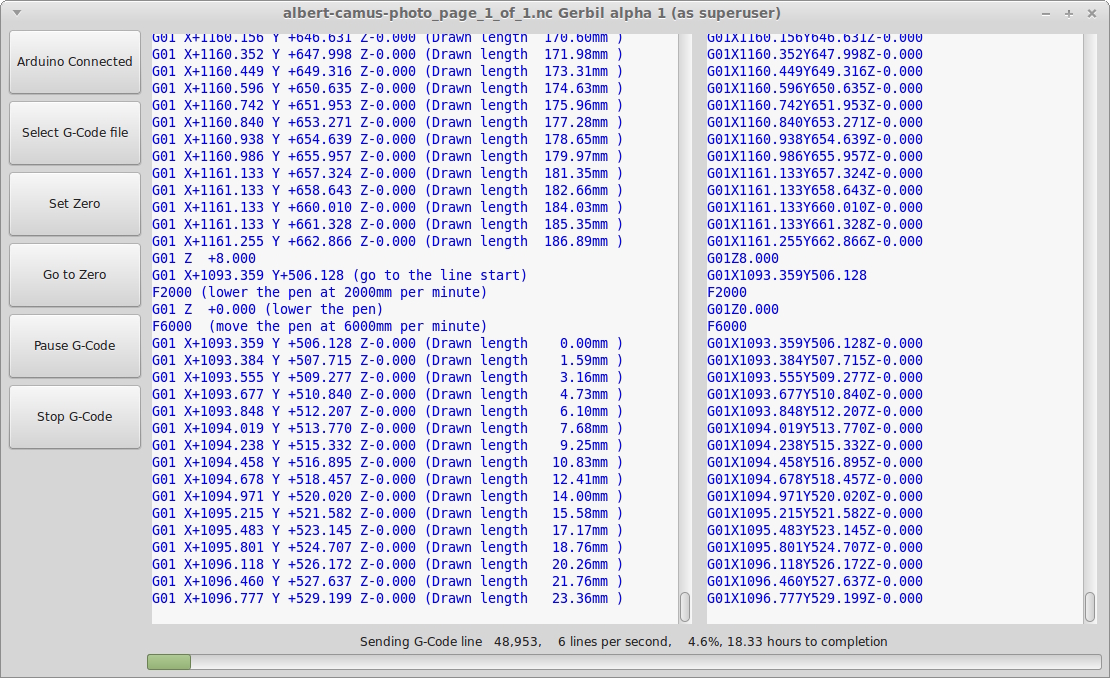
我正在使用 Linux 上的 GTK+3.0 在 C 中为 Grbl 编写 GUI。它是一个比其他 GUI 更简单的界面,因为我们的工作是 2D,Z 要求适中(绘图仪上的大型艺术绘图)。我正在使用带有规范协议的串行端口和到 Grbl 0.9j 的简单发送和确认接口
大多数 G 代码指令的距离非常短,约为 1 毫米,而且有很多。我发现大多数 G 代码行执行速度非常快(不到 100 毫秒),但有些行,尤其是在启动时,需要几秒钟。有时可能需要 Grbl 12 秒才能响应 G 代码行。
这是可以预料的还是我有错误?经过测量,运行 10,000 行 G 代码,我每秒处理大约 13 行。G 代码的进给速度设置为 6,000 毫米/分钟。
这是串行接口的低级代码:
`
#include “common_header.h”
#include “Arduino_serial_interface.h”
bool Grbl_is_connected = FALSE;
静态 int fd;
void show_terminal_options(struct termios *terminal_options)
{
printf(“———————————— ———————-\n”);
// — 控制终端输入的选项 — c_iflag
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & ICRNL) printf(“\ttranslate CR to NL on input\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & IXON) printf(“\t在输出上启用 XON/XOFF 流控制。\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & IXOFF) printf(“\t在输入上启用 XON/XOFF 流控制。\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & IXANY) printf(“\t键入任何字符将重新启动停止的输出。(The\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & IGNBRK) printf(“\t忽略输入中的 BREAK 条件。\n” );
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & BRKINT) printf(“\t如果设置了 IGNBRK,则忽略 BREAK。如果未设置但\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & IGNPAR) printf(“\tignore 帧错误和奇偶校验错误。\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & PARMRK) printf(“\t如果设置了这个位,输入字节有奇偶校验或帧错误\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & INPCK) printf(“\t启用输入奇偶校验。\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & ISTRIP) printf(“\t去掉第八位。\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & INLCR) printf(“\t在输入时将 NL 转换为 CR。\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & IGNCR) printf(“\输入时忽略回车。\n”);
if(terminal_options->c_iflag & IUTF8) printf(“\tcharacter-erase 在 cooked 模式下正确执行。\n”);
}
double compute_task_milli_seconds(struct timeval *start_time)
{
double elapsed_time;
结构 timeval 结束时间;
}
int write_arduino(char *g_code)
{
int n;
}
int read_arduino(char *response)
{
struct timeval start_time;
双毫秒;
诠释 n = 0;
}
int initialize_serial_port(const char *serial_port)
{
char Ctrl_X_Reset_Grbl[] = {CTRL_X, ‘\n’, ‘\0’};
结构 termios terminal_options;
布尔确定=假;
}
`